Understanding Types of Hearing Loss: Know The Causes

Hearing serves as a fundamental link to our world, shaping interactions and experiences. Consequently, hearing loss, a prevalent condition, disrupts daily life by reducing the ability to perceive sounds, spanning from mild to profound impacts across ages. Knowing the types of hearing loss possible will help you navigate the challenges.
The consequences of hearing loss transcend hearing alone, impacting social, emotional, and cognitive dimensions. Challenges include navigating conversations, missing crucial information, and feeling isolated in social settings. Struggling to decipher speech strains mental energy, leading to fatigue and diminished well-being. Acknowledging the importance of addressing hearing loss is paramount. So, this article interprets the diverse types of hearing loss, illuminating causes and treatments. If you’re wondering, “What are the causes of hearing loss?” read on.
What Are The Different Types of Hearing Loss?
In fact, comprehending the distinct hearing problem types is vital for selecting appropriate solutions, enabling individuals to address their unique auditory challenges effectively.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss:
Sensorineural hearing loss emerges from the inner ear (cochlea) or auditory nerve damage. Factors include aging, noise exposure, genetics, and medical conditions. Symptoms encompass speech comprehension difficulties, struggling in noisy settings, and perceived muffled sounds.
Conductive Hearing Loss:
Conductive hearing loss results from issues in the outer or middle ear. Causes range from earwax blockage to infections, perforated eardrums, or abnormal bone growth. So you’ll notice sound clarity, muffled hearing, and a sense of distant or faint sounds.
Mixed Hearing Loss:
Mixed hearing loss blends sensorineural and conductive factors. It can arise from combined inner and middle ear issues or separate causes. Symptoms meld characteristics of both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss.
Central Hearing Loss:
Central hearing loss pertains to impaired brain processing of auditory data, possibly due to damaged auditory pathways. Symptoms encompass speech comprehension challenges despite normal hearing and difficulty discerning sounds in complex auditory environments.
Temporary Hearing Loss:
Temporary hearing loss results from noise exposure, medications, infections, or pressure changes. It’s often reversible after addressing the underlying cause.
Understanding these types empowers informed decisions for managing hearing challenges effectively.
Learn more about medications that can cause hearing loss here.
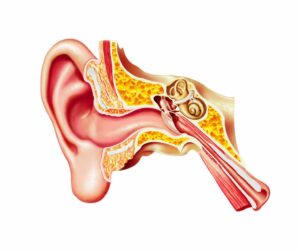
What Are the Causes of Hearing Loss?
Understanding the diverse causes of various hearing loss types is pivotal for preventive measures, early identification, and suitable interventions. So, safeguarding auditory health involves limiting noise exposure and monitoring ototoxic medications.
- Sensorineural hearing loss, often linked to age-related presbycusis, stems from gradual cochlear hair cell deterioration. High-frequency sound perception is particularly affected, hampering communication. However, loud noises and ototoxic drugs accelerate the process, which inflicts additional harm. Genetic factors and conditions like Meniere’s disease also contribute.
- Conductive hearing loss emerges when sound waves encounter barriers in the outer or middle ear. Earwax accumulation, infections, and ear bone irregularities impede sound transmission. Trauma or abrupt pressure changes can lead to perforated eardrums, disrupting sound conduction.
- Mixed hearing loss combines sensorineural and conductive elements arising from concurrent inner and middle ear issues. For instance, an existing sensorineural loss worsened by an ear infection results in a mixed type.
- Central hearing loss arises within the brain’s auditory processing centers, stemming from strokes, head injuries, or neurological disorders, affecting sound signal interpretation.
Regular hearing assessments benefit all types of hearing problems. Seeking expert guidance is vital for preserving and enhancing hearing abilities. Therefore, contact a hearing specialist so you don’t have to wonder what are the causes of hearing loss.

How Are the Common Types of Hearing Problems Treated?
Treating Common Types of Hearing Loss
Modern technological advancements offer treatments for various hearing loss types, enhancing communication and engagement with the auditory world, even if complete restoration of typical hearing is impossible.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss:
Sensorineural hearing loss, frequently permanent, finds effective solutions in hearing aids and cochlear implants. Hearing aids amplify sound, compensating for the diminished sensitivity of the cochlear hair cells. Cochlear implants, suitable for severe to profound cases, stimulate the auditory nerve directly, bypassing damaged hair cells. Early diagnosis through hearing tests is pivotal. Audiologists tailor interventions, selecting suitable devices based on individual hearing profiles.
Learn more about hearing aid features.
Conductive Hearing Loss:
Conductive hearing loss is typically reversible. Medical remedies, like earwax removal, antibiotics for infections, or surgical repairs of ear structures, can restore hearing function. A comprehensive assessment by an audiologist involves diverse tests, such as audiometry and tympanometry, to pinpoint the underlying cause. Surgical procedures can happen on an outpatient basis. Regular follow-ups ensure treatment efficacy.
Mixed Hearing Loss:
Managing mixed hearing loss necessitates personalized strategies that encompass sensorineural and conductive elements. Diagnosis involves identifying the causes behind the mixed type and tailoring interventions accordingly. Hearing specialists may recommend a combination of medical treatments, surgical procedures, or the use of hearing aids.
Central Hearing Loss:
Central hearing loss, stemming from brain-related factors, often benefits from auditory rehabilitation to train the brain to process sound signals more effectively. Audiologists evaluate cognitive capabilities and design programs targeting auditory processing. Precise diagnoses involve comprehensive evaluations, including speech perception tests, to identify central processing deficits.
Resources:
Individuals confronting hearing loss have access to a wealth of resources. Armed with expertise, audiologists assess, suggest interventions, and provide guidance. Also, support groups and virtual forums foster a sense of belonging and mutual understanding. Assistive listening devices help communication while captioning services and sign language interpretation cater to diverse needs. Public spaces are embracing inclusivity through enhanced accessibility initiatives like hearing loops.
Recognizing distinct hearing loss types and seeking professional assistance promptly is paramount. With the latest technologies and abundant resources, individuals can adeptly navigate their hearing challenges, fostering an enriched quality of life and refined communication abilities.
Understand more about why hearing loss treatment is important.

Next Steps to Understand Your Hearing Profile
Amid life’s symphony, hearing enriches experiences and connections. Yet, in this journey, hope and empowerment arise from understanding and intervention.
If hearing loss concerns you or a loved one, recognize that knowledge is the initial stride toward reclaiming a complete auditory spectrum. Knowing what are the causes of hearing loss will help you both. Stanford Hearing Aids is poised to accompany you on this path. Our dedicated care enables you to assess, treat, and grasp many types of hearing problems. Secure your free consultation now and embark on this transformative journey.
