The Science of Ear Wax: Why Removal is Sometimes Necessary

Understanding the Vital Role of Ear Wax
Ear wax, known scientifically as cerumen, is key to maintaining ear health. It’s not just a natural byproduct; it plays a critical role in protecting and preserving the functionality of our ears. Ear wax acts as a barrier against external elements, trapping dust, dirt, and other particles to protect the ear canal and eardrum. It also has antimicrobial and antifungal properties, helping to prevent infections. As a moisturizing agent, it keeps the ear canal from becoming dry and itchy, and it provides lubrication and protection for the eardrum. Ear wax even has a self-cleaning mechanism, gradually moving outwards to expel old particles. Typically, ear wax removal is something the body handles without help.
However, problems arise with overproduction or excessive buildup of ear wax. This can lead to temporary hearing loss, discomfort, and in rare cases, tinnitus. The variability in ear wax production among individuals sometimes necessitates professional intervention for its removal.
Understand more about types of tinnitus.
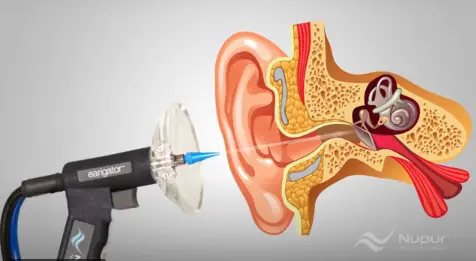
Professional Ear Wax Removal: What You Need to Know
Professional ear wax removal, or cerumen management, is a safe and necessary procedure when ear wax buildup leads to issues like hearing loss or ear discomfort. Specialists use various techniques, each chosen based on the ear wax’s consistency and the patient’s specific needs.
Irrigation:
- Method: This technique involves gently flushing the ear canal with a stream of warm water or saline solution.
- Purpose: The liquid softens the ear wax, making it easier to dislodge and remove.
- Suitability: It is often used for soft or moderate ear wax buildups and is ideal for those who may not tolerate more invasive procedures.
- Process: A syringe-like instrument is typically used to direct the fluid into the ear canal, washing away the wax.
- Considerations: Care must be taken to ensure the water temperature is comfortable to prevent dizziness or discomfort.
Manual Removal:
- Method: This involves using small, specialized tools like curettes, loops, or forceps.
- Purpose: These tools are designed to carefully scoop out, grasp, and remove the ear wax from the ear canal.
- Suitability: Manual removal is particularly effective for hard, impacted ear wax that can’t be easily flushed out.
- Process: The procedure is often performed under the guidance of a microscope or magnifying lens for precision.
- Considerations: This method requires a steady hand and detailed knowledge of ear anatomy to avoid injury to the ear canal or eardrum.
Microsuction:
- Method: Microsuction uses a low-pressure suction device to vacuum out ear wax gently.
- Purpose: This method provides a clean, quick, and safe way to remove ear wax without the need for liquids.
- Suitability: It is highly effective for all types of ear wax, especially when it is hard, impacted, or located deep in the ear canal.
- Process: An audiologist or trained professional uses a microscope to view the ear canal in detail while performing the suction.
- Considerations: Microsuction is regarded as a very safe and comfortable method, with minimal risk of infection or damage to the ear.
Each of these methods offers a safe and effective way to address ear wax buildup, and the choice of technique often depends on the individual’s specific situation and the nature of their ear wax. Professionals will assess the condition of the ear and ear wax to determine the most appropriate method for removal.
Recognizing When You Need Professional Ear Wax Removal
Understanding when to seek professional help is crucial. Symptoms of ceruminosis, or excessive ear wax accumulation, include:
- Significant hearing loss
- Persistent ear discomfort or pain
- Unusual ear drainage or odor
- Visible earwax blockage
- Impacted earwax resistant to home methods
Over-the-counter ear drops may offer temporary relief, but professional removal is often the safer and more effective solution, especially for older adults or those with higher ear wax production.
Where Can I Get Professional Ear Wax Removal?
When considering ear wax removal, evaluate your comfort level with the procedure, the cost, and insurance coverage. It’s important to choose a qualified and experienced provider. If you’re searching for “ear wax removal near me,” consider these options:
- Doctor’s Office: For assessment and possible removal.
- Local Hearing Center: Specialists like audiologists are equipped for safe removal.
- Urgent Care Center: For immediate symptoms requiring attention.
Read more about what audiologists do.
What to Expect During an Ear Wax Removal Appointment: A Detailed Overview
When you visit a specialist for an ear wax removal appointment, the experience typically involves several key steps:
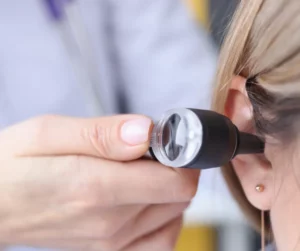
Initial Examination:
The specialist, often an audiologist or a trained healthcare provider, will start by examining your ear using an otoscope.
This instrument allows them to view the ear canal and eardrum clearly, assessing the extent of the ear wax buildup and checking for any signs of infection or damage.
Choosing the Removal Method:
Depending on the nature and amount of wax, the specialist will select the most appropriate removal method, which could be irrigation, manual removal, or microsuction.
They will explain the chosen method and what you can expect during the procedure.
The Removal Process:
If irrigation is used, a controlled stream of warm water or saline solution will be directed into the ear to soften and wash away the wax.
In the case of manual removal, specialized tools will gently extract the wax.
For micro suction, a gentle suction device is used to vacuum the wax out.
Sensitivity Post-Removal:
After the ear wax is removed, you might experience heightened sensitivity to sound as the blockage that muffled sound is gone. This heightened sensitivity is usually temporary and should normalize soon.
Post-Procedure Care:
The specialist may provide ear ointments or drops to soothe the ear canal after the procedure and to assist with any residual irritation. They will also offer advice on aftercare to ensure proper healing.
Aftercare and Preventing Future Ear Wax Build-Up
Maintaining ear health after the removal procedure is important to prevent future problems:
- Avoid Cotton Swabs: Using cotton swabs can push wax deeper into the ear canal, leading to impaction. It’s best to avoid them for internal ear cleaning.
- Hearing Aid Care: Regularly clean and maintain hearing aids. Moisture can exacerbate wax buildup, so keep them dry.
- Regular Ear Checks: Schedule routine appointments for earwax assessment and removal, especially if you’re prone to frequent buildups.
- Manage Contributing Factors: Address any underlying health conditions, like skin disorders, that may contribute to excessive ear wax production.
- Routine Cleaning Appointments: For those with recurrent issues, scheduling regular cleanings with a specialist can be helpful.
- Device Cleanliness: Keep earbuds, hearing aids, and other ear devices clean to minimize wax buildup.
Following these steps can help ensure your ears remain healthy and free from excessive wax buildup. If you have concerns about your ear health or experience symptoms like hearing loss or discomfort, consult a specialist for a professional evaluation and treatment.
Prioritizing Ear Health with Expert Care
In summary, ear wax plays a pivotal role in our auditory health, but professional intervention is necessary when its buildup becomes problematic. Regular maintenance and understanding when to seek professional care are key to preventing complications. If you’re facing any earwax-related issues or have concerns about your ear health, we are here to provide expert, safe, and comfortable ear wax removal services. Contact Stanford Hearing to ensure your ears are well-cared for, allowing you to enjoy the world of sound with clarity and comfort.
