Reduce Ear Wax: The Do’s and Don’ts
Updated December 8th, 2025
Discover the intriguing world of ear health as we dive into the secrets of how to reduce ear wax. From foods that can help minimize wax buildup to hands-on techniques for massaging that stubborn ear wax away, we’ve got you covered. Plus, learn when it’s high time to seek expert ear cleaning. Get ready for some ear-responsible advice you won’t want to miss!
Why Does Ear Wax Exist?
Ear wax, also known as cerumen, serves vital functions in maintaining your ear health. Composed of a unique mix of fatty acids, cholesterol, and dead skin cells, this substance is more than meets the eye.
Key Roles of Ear Wax:
Ear wax works behind the scenes to protect your hearing system in multiple ways.
- Skin Guardian: Keeps your ear canal’s delicate skin moisturized, warding off dryness and itchiness.
- Cleanser: Helps remove debris and dead skin cells, ensuring clean ears.
- Infection Fighter: Fends off bacteria and fungi, lowering your risk of ear infections.
- Foreign Object Filter: Traps incoming dirt and dust, acting as your ear canal’s first line of defense.
- Waterproof Barrier: Blocks water from infiltrating your ears, reducing infection risk.
- Eardrum Defender: Serves as a protective shield for your sensitive eardrum.
While ear wax has its perks, too much can cause problems like hearing loss and ear blockages. If you’re facing such issues, explore how to reduce ear wax effectively. Just remember, a balanced amount of earwax is often your ears’ best friend. Have more hearing health questions answered.
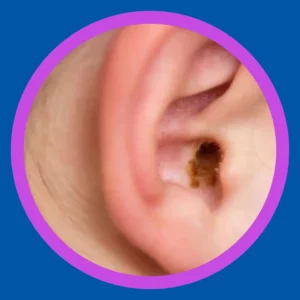
Understanding Ear Wax Buildup: Causes and Solutions
Identifying the reasons behind ear wax accumulation is essential for proactive ear health. Numerous factors can lead to this buildup, and understanding them helps you take preventive action.
Common Causes of Buildup:
Several physical and lifestyle factors contribute to excess ear wax production and retention.
- Anatomical Factors: Narrow or hairy ear canals can trap earwax, hindering its natural exit.
- Overproduction: Genetics or aging can lead some people to produce excess earwax.
- Lifestyle Choices: Regular use of earbuds, earplugs, or cotton swabs can worsen the buildup.
- Medical Conditions: Issues like eczema and psoriasis can accelerate earwax production.
- Hearing Aids: These devices can trap earwax, preventing it from draining naturally.
- Aging: As you age, earwax becomes drier, increasing impaction risk.
Your daily habits play a bigger role than you might think. Frequent insertion of objects into your ear canal triggers increased wax production as a protective response. This creates a frustrating cycle where attempted cleaning actually makes the problem worse.
Recognizing Symptoms
Awareness of earwax buildup symptoms ensures timely intervention. Your body sends clear signals when wax accumulation becomes problematic.
- Earache, often a dull, continuous pain, signals possible blockage.
- Tinnitus, characterized by ear ringing, indicates affected auditory pathways.
- Itching and irritation often accompany buildup.
- Reduced hearing or ear “fullness” are common complaints.
- Less commonly, you might experience a foul odor, dizziness, reflex coughing, or hearing aid malfunction.
These symptoms shouldn’t be ignored. What starts as mild discomfort can progress to more serious complications if left untreated. Early recognition means easier resolution.
Treatment Techniques
If you experience these symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. Understanding your options helps you make informed decisions about how to reduce ear wax effectively.
- Limiting hearing aid usage helps curb earwax accumulation.
- Over-the-counter ear drops assist in natural earwax removal.
- Simple ear massages can help the wax move naturally out of the ear canal.
- Professional methods, like ear irrigation, micro-suction, and curette, offer effective solutions for persistent buildup.
Each approach has its place depending on the severity of your situation. Mild cases often respond well to home care, while stubborn impactions require professional cerumen removal.
Effective Techniques for Massaging Ear Wax Out
While not a replacement for medical intervention, knowing how to massage ear wax out can offer temporary relief from the discomfort of earwax buildup. Many people find this technique helpful when waiting for professional treatment. The massage method works by encouraging natural ear wax migration through gentle manipulation.
Step-by-Step Massage Instructions
Start by finding a quiet, comfortable space where you can focus. Position yourself comfortably, either sitting or standing. Place your index and middle fingers behind your earlobe, near your ear’s base. Apply gentle pressure and engage in slow, circular motions to help dislodge the earwax.
While massaging, integrate some earlobe tugging. Open and close your mouth while doing so. This combination can further help to loosen stubborn earwax. The jaw movement creates subtle shifts in your ear canal structure, facilitating wax movement.
As you continue, slightly tilt your head to one side. This will encourage the loosened earwax to exit the ear canal. Gravity becomes your ally in this process, allowing softened wax to work its way outward naturally.
Timing and Frequency
Repeat these steps on the other ear, being mindful not to exert too much pressure. Keep each massage session brief to prevent irritation. Most experts suggest limiting sessions to three to five minutes per ear.
You can perform this technique once or twice daily if needed. Consistency matters more than intensity. Gentle, regular massage proves more effective than aggressive, infrequent attempts.
If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. While learning how to massage ear wax out can offer temporary relief, it shouldn’t replace professional advice on how to reduce ear wax.

What to Avoid to Reduce Ear Wax
Managing earwax effectively requires caution, as some common approaches can aggravate the issue or cause injury. Understanding what not to do proves just as important as knowing proper techniques. Here’s what you should steer clear of:
Dangerous DIY Methods
Popular doesn’t mean safe when it comes to ear care. Several widely promoted methods can cause serious harm.
- Steer Clear of Cotton Swabs: Despite their popularity, cotton swabs can push earwax deeper into your ear canal. Medical experts advise against their use for earwax removal.
- Skip Home Suction Devices: Items like Wax-Vac® generally fall short of effectiveness, and most healthcare providers caution against their use.
- Beware of Ear Candles: Promoted as a natural solution, ear candles are ineffective and dangerous. They risk causing burns, ear canal damage, and even eardrum perforation.
- Avoid Unproven DIY Methods: Vacuum kits and other at-home remedies lack scientific evidence and are often less safe and effective than professional treatment.
The appeal of quick fixes is understandable, but ear health demands evidence-based approaches. What seems harmless can lead to expensive complications requiring medical intervention. Understanding the science of ear wax helps you make safer choices.
Why Professional Care Matters
For persistent or worsening symptoms, consult a hearing care provider or audiology expert for appropriate advice and treatment. We have cerumen removal services at Stanford Hearing Aids, for example. Professional tools and training make removal safer and more effective than home attempts.
Are There Foods That Reduce Ear Wax?
While scientific evidence doesn’t directly link specific foods that reduce ear wax, maintaining a balanced diet can promote overall ear health. A nutrient-rich diet may help in the indirect management of ear wax levels. Think of nutrition as supporting your body’s natural ear cleaning system.
Key Nutrients and Their Sources
Certain vitamins and minerals play crucial roles in maintaining healthy ear function and proper wax consistency.
- Anti-Inflammatory Omega-3s: Oily fish like salmon, mackerel, and tuna offer Omega-3 fatty acids, which can mitigate inflammation in ear canals.
- Antioxidant-Rich Fruits and Vegetables: Consuming oranges, sweet potatoes, and spinach provides essential vitamins and antioxidants that can safeguard your ear canals against oxidative damage.
- Whole Grains: Foods high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals like zinc, such as whole grains, can promote both digestive and ear health.
- Vitamins for Immunity: Incorporate foods rich in Vitamins A, C, and E like nuts and sweet potatoes to strengthen your immune system and possibly reduce inflammation.
- Zinc-Packed Choices: Include legumes, nuts, and whole grains in your diet for a zinc boost, which is vital for ear health.
- Hydration: Drinking enough water can soften earwax and prevent the ear canal from drying, reducing the chances of excessive earwax formation.
Although no foods directly reduce ear wax, a well-rounded diet can help maintain ear health. These nutritional strategies support your body’s natural ability to regulate wax production and consistency. For ongoing issues, seek advice from a qualified hearing care provider.
The Hydration Connection
Water deserves special attention in ear health discussions. Adequate hydration affects mucus membrane function throughout your body, including your ear canals. Dehydrated tissue produces thicker, stickier secretions that don’t migrate as easily. Aim for eight glasses daily to support optimal ear wax consistency.
When to Seek Professional Help
Knowing when to handle ear wax at home versus seeking professional assistance can prevent complications and protect your hearing. Not every situation calls for a doctor’s visit, but certain signs demand professional attention.
Professional vs. Home Care Decision Guide
| Seek Professional Help When: | Safe for Home Care When: |
|---|---|
| You experience sudden hearing loss in one or both ears | You notice mild ear fullness without pain |
| Severe pain persists despite home treatment attempts | Slight discomfort improves with massage or drops |
| You see discharge, bleeding, or fluid from your ear | Your symptoms are mild and intermittent |
| Dizziness or balance problems accompany ear symptoms | You have a history of successful home management |
| You have a perforated eardrum or ear surgery history | Over-the-counter drops provide relief within days |
| Objects are lodged in your ear canal | You’re simply maintaining regular ear health |
| Symptoms worsen after using home remedies | You want preventive care before issues develop |
This table helps you make informed decisions about your ear care approach. When in doubt, professional evaluation provides peace of mind and prevents potential complications.
Finding Local Expertise
If you need professional assessment, local hearing centers offer ear wax removal with specialized equipment and trained providers. These facilities use safe, effective techniques impossible to replicate at home. Professional removal typically takes just minutes and provides immediate relief.
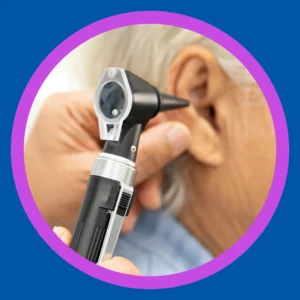
Understanding Medical Removal Methods
Professional ear wax removal involves several specialized techniques, each suited to different situations. Healthcare providers select methods based on wax consistency, location, and your individual anatomy.
Common Professional Techniques
Irrigation uses warm water to flush out softened wax. This gentle method works well for moderate buildup without complications. Micro-suction employs a tiny vacuum to extract wax under microscopic visualization. It’s particularly effective for hard, impacted wax.
Manual removal with a curette involves using a small, curved instrument to scoop out wax. This precise technique suits situations where other methods aren’t appropriate. Your provider determines the best approach after examination.
Most procedures cause minimal discomfort and take less than thirty minutes. Many patients report immediate hearing improvement following professional removal. The relief often exceeds expectations for those who’ve struggled with home methods.
Prevention Strategies for Long-Term Success
Once you’ve addressed existing buildup, prevention becomes your next priority. Smart habits reduce the likelihood of future problems and maintain optimal ear health.
Daily Ear Care Best Practices
Avoid inserting anything into your ear canal, including fingers. External cleaning with a damp cloth suffices for most people. Let your ears’ natural cleaning mechanism do its job.
Use ear protection in dusty or dirty environments. Construction sites, woodworking areas, and similar spaces expose your ears to debris that can mix with wax. Simple foam plugs provide adequate protection.
If you use hearing aids, clean them regularly according to manufacturer instructions. Wax buildup on devices leads to increased canal accumulation. Daily wiping prevents this cycle.
When Regular Monitoring Helps
Some individuals naturally produce more ear wax or have anatomical features that promote buildup. If you fall into this category, schedule periodic professional cleanings every six to twelve months. Preventive visits prove easier and more comfortable than emergency interventions.
Next Steps in How to Reduce Ear Wax
Ear health involves a balanced approach, from understanding the role of earwax to knowing when professional intervention is necessary. Whether it’s incorporating certain nutrients into your diet or avoiding common mistakes in earwax removal, your ears deserve attentive care. The strategies outlined here provide a comprehensive framework for maintaining healthy ears throughout your life.
If you’re dealing with persistent or worsening symptoms related to earwax buildup, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and effective treatment. Self-treatment has limits, and recognizing those boundaries protects your hearing.
At Stanford Hearing, we specialize in comprehensive hearing care, including professional cerumen removal services. Don’t let earwax buildup affect your quality of life. Contact Stanford Hearing Aids today for professional ear care solutions tailored to your needs.
